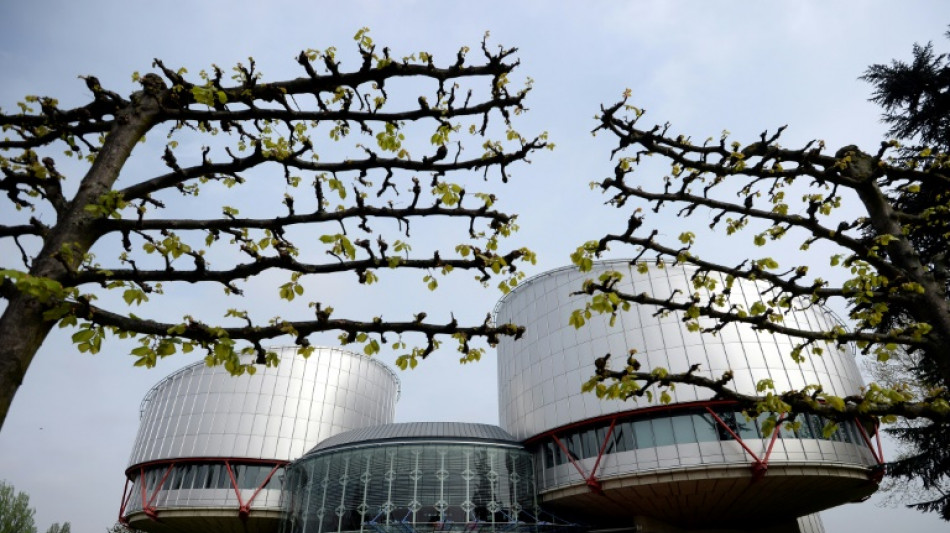
European rights court upholds French ban on posthumous procreation
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) on Thursday upheld France's ban on procreation using stored gametes or embryos originating from a person who has since died.
The judges considered the cases of two women born in 1992, who had sought to have frozen sperm or embryos from their deceased partners transferred to Spain, where posthumous procreation is legal.
One couple, who had been together for 11 years, had sperm frozen soon after the man was diagnosed with brain cancer.
But the woman was unable to conceive a baby through artificial insemination before her husband died in 2019.
She asked that the stored gametes be exported to Spain.
A second woman had already had two children with her husband, the second born through in-vitro fertilisation as the man began suffering from leukaemia.
They were able to store five embryos in 2018, with the woman asking that they be transferred to Spain the following year.
Both women appealed to the ECHR after French authorities refused to allow the transfers.
France's public health code bars posthumous procreation, as well as export of gametes or embryos for purposes illegal under French law.
But the women argued that the government was breaching their rights under Article 8 of the European Convention on Human Rights, which guarantees respect for private and family life.
- 'A fair balance' -
The European judges found that "domestic authorities had struck a fair balance between the competing interests at stake" and that Paris was "within its discretion" to determine how to treat gametes and embryos.
"In making the contested requests, the applicants' sole aim had been to circumvent French law... they had not put forward any particular arguments that would have justified the law not being applied in their cases," the court said in a statement.
The judges did have one reservation, noting that since 2021 single women and lesbian couples have been able to have children through medically assisted reproduction.
This "reopened the debate as to the relevance of the justification for maintaining the prohibition" on posthumous procreation, they said.
"The Court reiterated that, while (member) states enjoyed a wide discretion in the bioethical sphere, the legislative framework put in place by them had to be coherent," the statement read.
Elsewhere in Europe, Portuguese woman Angela Ferreira last month gave birth to a baby born from the frozen sperm of her dead husband, after her campaigning got a similar ban overturned in 2021.
A.Soto--LGdM