Brazil sees dengue cases quadruple ahead of vaccine drive
The number of dengue fever cases in Brazil since January 1 is four times higher than the same period last year, government data showed Saturday, ahead of the launch of a vaccination campaign.
In the first four weeks of 2024, 262,247 probable cases were recorded, compared to 65,366 in the same period last year, according to the latest figures available from the Brazilian Health Ministry's database.
Fabio Baccheretti, president of the National Council of Health Secretaries, pointed to high temperatures as a major factor behind the spread of the mosquito-born illness.
"The record temperatures at the end of last year, with the El Nino phenomenon, are a new and determining factor," he told AFP.
Dengue fever has killed 29 people this year in Latin America's largest country, and an additional 173 deaths are being evaluated for possible links to the disease.
Mosquito-borne dengue, which can cause hemorrhagic fever, infects an estimated 100 million to 400 million people yearly around the world, although most cases are mild or asymptomatic, the World Health Organization says.
"We are seeing that dengue is spreading in areas that were previously free in Brazil, so we must follow this phenomenon closely," Baccheretti warned.
Health services are already under strain in many metropolitan areas in Brazil due to the rising caseload.
In the capital district of Brasilia, a field hospital will begin receiving dengue patients starting next week.
The most affected state thus far is southeast Minas Gerais, the second most populated in Brazil, with more than 88,587 probable cases reported.
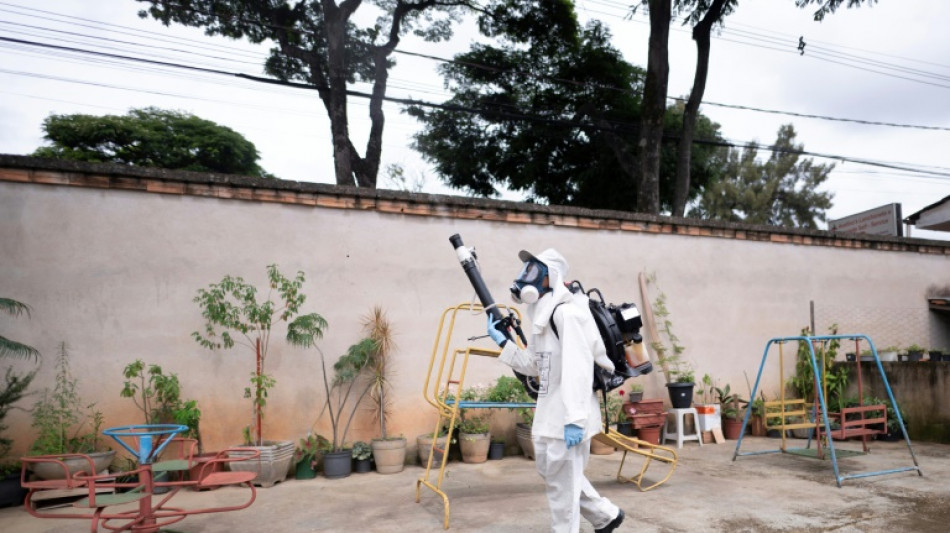
Outside the state capital of Belo Horizonte, teams of fumigators are going door-to-door as part of a campaign against disease-spreading mosquitos.
Members are equipped with gas masks and dressed in white head-to-toe coveralls.
"It's sometimes difficult to get into people's homes, but they're starting to see that there are a lot of cases around them and are becoming more understanding," said supervisor Katia Batista.
Two weeks ago, the Brazilian government announced that a free vaccination campaign targeting 3.2 million people would take place in February, with priority given to children aged 10 to 14, the group with the highest number of hospitalizations.
However, available doses are limited due to a shortage of supply from the vaccine's developer, Japanese pharmaceutical company Takeda, Brazil's health ministry said.
In all, the nation of 203 million people expects this year to receive 6.5 million doses of the two-dose vaccine, which is tailored for children.
U.Romero--LGdM